









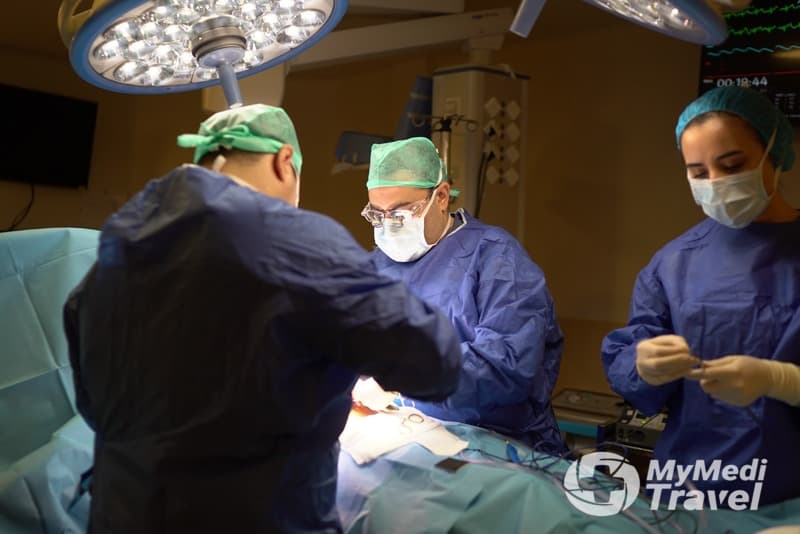
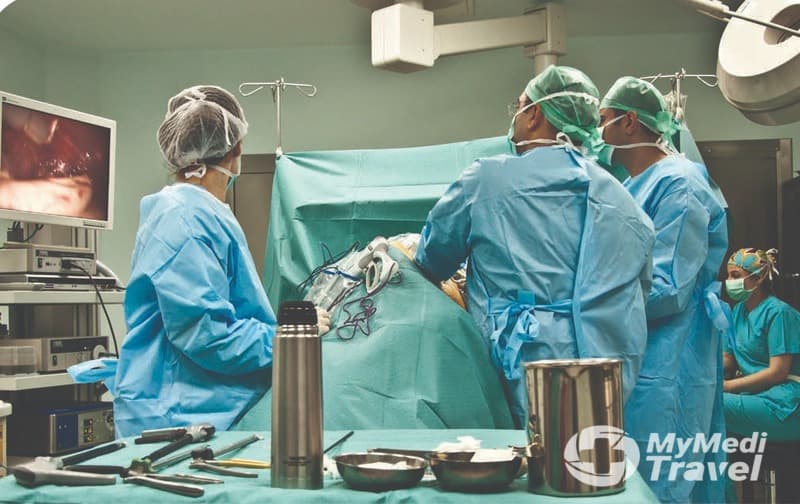












Gastric balloon
What type of method is a Gastric balloon?
It is a method that is applied for the treatment of obesity and that requires no surgery. It is a method that helps lose weight and enables a low-calorie environment as a result of less food intake and continuous satiety thanks to the balloon covering a big volume in the stomach. The balloon can stay in the stomach for 6 to 12 months as it is a method administered for the treatment of obesity for nearly 30 years now. A weight loss of nearly 20 kg. can be expected in one year as long as he/she follows a strict diet and does exercise.
The weight is monitored based on a diet supervised by a dietitian after the placement of the balloon.
Who is eligible for the gastric balloon?
Patients with BMI ≥ 30
Patients who fail to lose weight even though they follow many diets and do exercises.
Obese patients for whom a surgical procedure would be a risk
Patients over the age of 18 and under the age of 60
Who is not eligible for the gastric balloon?
Alcohol and drug addicts
Pregnant patients and those planning to get pregnant,
Those with a severe cardiac, renal, liver, or pulmonary disease
Patients with a history of esophageal and gastric surgery
Patients who need to be on blood thinners all the time
Patients with gastrocele, reflux, and esophageal burn
Patients with gastric-duodenal ulcer
How to Place Gastric Balloon?
The balloon is endoscopically placed, that is to say without surgery. The patients are anesthetized and do not feel anything during the procedure, which is performed in 15 minutes on average.
Before the balloon is placed, the esophagus, stomach, and duodena are endoscopically examined to see if there is any barrier to the placement of the balloon. In patients with no barriers, the balloon is forwarded to the stomach through the mouth and esophagus by means of a special apparatus after the endoscope is removed. After the endoscopy is performed and the position of the balloon in the stomach is established, the balloon is inflated by pumping methylene blue-dyed saline into it by means of special endoscopic apparatuses. 400 cc of saline, which is an initial dose, can be increased over time depending on the tolerability of patients and all these procedures are performed endoscopically. Patients wake up right after the procedure and are discharged after being hospitalized for a couple of hours.
Does gastric balloon rupture? How to tell if it is ruptured and how to respond?
The rupture of a gastric balloon is a rare case. When it is ruptured, the blue liquid inside goes into the intestines and dye the urine blue. Patients excrete the balloon in natural ways or it is endoscopically removed.
What are the side effects of the placement of gastric balloon?
The placement of a gastric balloon may cause bleeding and rupture one's esophagus and stomach, though rarely.
Patients may initially feel a sense of discomfort in the stomach, nausea and/or vomit. This can be taken under control by orally or intravenously administered medication and patients get used to the balloon over time. They may feel tired and weak in the early weeks as a result of reduced intake of fluids.
The ruptured balloon goes into the intestines and may cause intestinal blockage that would require a surgical procedure.
What does Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals offer patients?
How many specialists are there and what accreditation's have been awarded to Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals?
The Gastric Balloon Treatment is a non-surgical system meant to assist in controlling caloric intake and fostering a healthy way of life. This process places a saline-crammed balloon to your belly as a brief weight reduction answer. It can be a compelling choice for people searching for to shed pounds and construct healthful behavior without resorting to invasive surgery.
It is critical to know that Gastric Balloon Treatment isn't a magic bullet but a device to help in your weight loss journey. You will want to commit to a more fit weight loss program and regular workouts to achieve sustainable consequences.
Recovery time for a Gastric Balloon Treatment can range relying on the character's standard fitness, how properly the technique went, and the individuals response to healing. Most people go through some stage of discomfort in the initial days following the method, with nausea and vomiting being commonplace. Normally, those signs and symptoms subside inside per a week because the body adjusts to the gastric balloon.
As the Gastric Balloon Treatment is nonsurgical, you might be capable of resuming typical day-by-day activities within a couple of days. A follow-up appointment along with your healthcare professional is commonly scheduled within a week of the procedure, to evaluate your recuperation and provide nutritional pointers. Speak with your healthcare professional for a more correct estimation of restoration times based on your particular circumstances.
The success rate of Gastric Balloon Treatment can vary widely, relying in large part at the commitment of the man or woman to make large life-style adjustments. On common, patients can expect to lose approximately 15% to twenty-five% in their extra body weight during the six months the balloon is in vicinity.
However, the lengthy-time period fulfillment of this procedure relies upon on preserving the life-style modifications initiated all through the balloon treatment length. Those who return to dangerous eating conduct after the balloon is eliminated may want to regain the misplaced weight. It is important, therefore, to take a look at Gastric Balloon Treatment as an initial step in a long-time period weight control strategy.









































Gastric balloon
What type of method is a Gastric balloon?
It is a method that is applied for the treatment of obesity and that requires no surgery. It is a method that helps lose weight and enables a low-calorie environment as a result of less food intake and continuous satiety thanks to the balloon covering a big volume in the stomach. The balloon can stay in the stomach for 6 to 12 months as it is a method administered for the treatment of obesity for nearly 30 years now. A weight loss of nearly 20 kg. can be expected in one year as long as he/she follows a strict diet and does exercise.
The weight is monitored based on a diet supervised by a dietitian after the placement of the balloon.
Who is eligible for the gastric balloon?
Patients with BMI ≥ 30
Patients who fail to lose weight even though they follow many diets and do exercises.
Obese patients for whom a surgical procedure would be a risk
Patients over the age of 18 and under the age of 60
Who is not eligible for the gastric balloon?
Alcohol and drug addicts
Pregnant patients and those planning to get pregnant,
Those with a severe cardiac, renal, liver, or pulmonary disease
Patients with a history of esophageal and gastric surgery
Patients who need to be on blood thinners all the time
Patients with gastrocele, reflux, and esophageal burn
Patients with gastric-duodenal ulcer
How to Place Gastric Balloon?
The balloon is endoscopically placed, that is to say without surgery. The patients are anesthetized and do not feel anything during the procedure, which is performed in 15 minutes on average.
Before the balloon is placed, the esophagus, stomach, and duodena are endoscopically examined to see if there is any barrier to the placement of the balloon. In patients with no barriers, the balloon is forwarded to the stomach through the mouth and esophagus by means of a special apparatus after the endoscope is removed. After the endoscopy is performed and the position of the balloon in the stomach is established, the balloon is inflated by pumping methylene blue-dyed saline into it by means of special endoscopic apparatuses. 400 cc of saline, which is an initial dose, can be increased over time depending on the tolerability of patients and all these procedures are performed endoscopically. Patients wake up right after the procedure and are discharged after being hospitalized for a couple of hours.
Does gastric balloon rupture? How to tell if it is ruptured and how to respond?
The rupture of a gastric balloon is a rare case. When it is ruptured, the blue liquid inside goes into the intestines and dye the urine blue. Patients excrete the balloon in natural ways or it is endoscopically removed.
What are the side effects of the placement of gastric balloon?
The placement of a gastric balloon may cause bleeding and rupture one's esophagus and stomach, though rarely.
Patients may initially feel a sense of discomfort in the stomach, nausea and/or vomit. This can be taken under control by orally or intravenously administered medication and patients get used to the balloon over time. They may feel tired and weak in the early weeks as a result of reduced intake of fluids.
The ruptured balloon goes into the intestines and may cause intestinal blockage that would require a surgical procedure.
What does Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals offer patients?
How many specialists are there and what accreditation's have been awarded to Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals?


















Gastric balloon
What type of method is a Gastric balloon?
It is a method that is applied for the treatment of obesity and that requires no surgery. It is a method that helps lose weight and enables a low-calorie environment as a result of less food intake and continuous satiety thanks to the balloon covering a big volume in the stomach. The balloon can stay in the stomach for 6 to 12 months as it is a method administered for the treatment of obesity for nearly 30 years now. A weight loss of nearly 20 kg. can be expected in one year as long as he/she follows a strict diet and does exercise.
The weight is monitored based on a diet supervised by a dietitian after the placement of the balloon.
Who is eligible for the gastric balloon?
Patients with BMI ≥ 30
Patients who fail to lose weight even though they follow many diets and do exercises.
Obese patients for whom a surgical procedure would be a risk
Patients over the age of 18 and under the age of 60
Who is not eligible for the gastric balloon?
Alcohol and drug addicts
Pregnant patients and those planning to get pregnant,
Those with a severe cardiac, renal, liver, or pulmonary disease
Patients with a history of esophageal and gastric surgery
Patients who need to be on blood thinners all the time
Patients with gastrocele, reflux, and esophageal burn
Patients with gastric-duodenal ulcer
How to Place Gastric Balloon?
The balloon is endoscopically placed, that is to say without surgery. The patients are anesthetized and do not feel anything during the procedure, which is performed in 15 minutes on average.
Before the balloon is placed, the esophagus, stomach, and duodena are endoscopically examined to see if there is any barrier to the placement of the balloon. In patients with no barriers, the balloon is forwarded to the stomach through the mouth and esophagus by means of a special apparatus after the endoscope is removed. After the endoscopy is performed and the position of the balloon in the stomach is established, the balloon is inflated by pumping methylene blue-dyed saline into it by means of special endoscopic apparatuses. 400 cc of saline, which is an initial dose, can be increased over time depending on the tolerability of patients and all these procedures are performed endoscopically. Patients wake up right after the procedure and are discharged after being hospitalized for a couple of hours.
Does gastric balloon rupture? How to tell if it is ruptured and how to respond?
The rupture of a gastric balloon is a rare case. When it is ruptured, the blue liquid inside goes into the intestines and dye the urine blue. Patients excrete the balloon in natural ways or it is endoscopically removed.
What are the side effects of the placement of gastric balloon?
The placement of a gastric balloon may cause bleeding and rupture one's esophagus and stomach, though rarely.
Patients may initially feel a sense of discomfort in the stomach, nausea and/or vomit. This can be taken under control by orally or intravenously administered medication and patients get used to the balloon over time. They may feel tired and weak in the early weeks as a result of reduced intake of fluids.
The ruptured balloon goes into the intestines and may cause intestinal blockage that would require a surgical procedure.
What does Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals offer patients?
How many specialists are there and what accreditation's have been awarded to Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals?
CONTACT SUCCESSFUL