









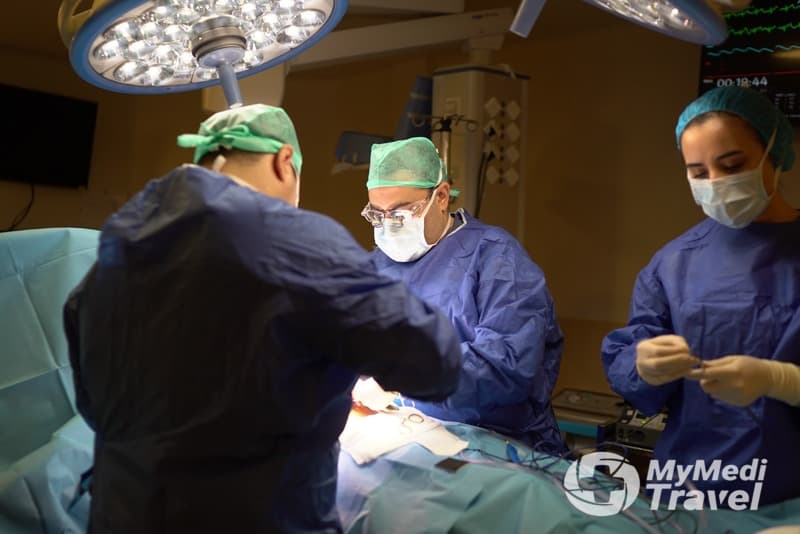
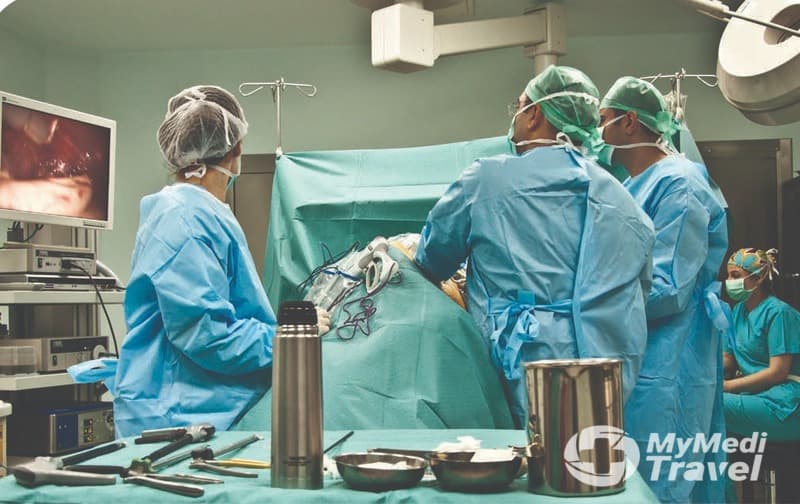












Hip and Knee Joint Replacement Surgery
Total joint replacement is a surgical procedure where parts of an arthritic or damaged joint are removed and replaced with a metal, plastic or ceramic device called a prosthesis or implant. The prosthesis is designed to reproduce the shape and motion of the normal joint.
A joint is an area in the body where two or more bones join together to allow motion. The surfaces of the bones are covered with cartilage to form a normal smooth gliding joint. Over time this cartilage can break down, leading to bone-on-bone friction which can cause inflammation and pain.
The most common conditions that lead to joint replacement surgery are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. There are, however, other causes of joint pain that may also lead to joint replacement including hereditary disorders, developmental problems, and trauma. Joint replacement is performed only after other conservative treatments have failed such as medications, physical therapy, and injections.
Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
We successfully perform partial and total joint prostheses in our Prosthetic Surgery Department. Total joint prosthesis aims to stabilize the joint by replacing the damaged joint surface with artificial materials and to eliminate existing pain. In recent years, total joint prosthesis practices having increasingly been performed in our country as in the whole world.
The joints where prosthetic surgery is mostly performed are knee and hip prostheses. It is also frequently used in the treatment of deformations in the cartilage surfaces of the joints due to arthritis, infections, rheumatic diseases, trauma, or congenital structural disorders.
We perform general anesthesia or local anesthesia (spinal and/or epidural) for our hip and knee replacement surgeries. We take the choices jointly with our patients. Generally, within the first 48 hours after prosthesis surgery, we get our patients to stand up and walk.
What Happens During Joint Replacement Surgery
Hip and knee replacement are two of the most commonly performed operations in orthopedic surgery. Both procedures are very successful at eliminating pain, correcting deformity and improving patient mobility so patients can regain quality of life and get back to the activities they enjoy.
During hip replacement, the damaged ball of the hip ball and socket joint is removed and replaced with a metal or ceramic ball that attaches to a stem that fits into the femur. The prosthesis is usually coated with a special material into which the bone will grow over time. In some instances, however, the prosthesis is cemented into the bone. The socket portion of the ball and socket joint is also replaced with a metal cup that is placed into the pelvis. A plastic liner is then snapped into the metal cup and rotates with the new ball on the end of the femoral stem. The prostheses and implants come in a variety of shapes and sizes that can be tailored to the individual.
During total knee replacement surgery, a thin amount of bone along the surface of the joint is removed from the end of the femur or thigh bone, the top of the tibia or leg bone, as well as the underside of the kneecap. The surfaces of the bone are then shaped with tools and sized to allow an appropriate implant fit for each individual knee. The major ligaments and tendons of the knee are typically kept in place to provide stability and normal motion of the knee joint. Like hip replacements, knee replacements can either be cemented into place or are covered in a special material into which the bone will grow.
Total joint replacement surgery usually takes one to two hours and is typically performed in a hospital setting with a one- to two-day hospital stay. The procedure is usually performed under spinal anesthesia in combination with a nerve block. This prevents the need for general anesthesia and intubation during the surgery and can help patients avoid many of the side effects of general anesthesia such as post-operative nausea. This allows for better pain control and quicker recovery.
Following the surgery and a short stay in the recovery room, patients will begin walking on the day of their surgery. The majority of patients are then sent home with instructions for further therapy. Typically, patients can return to work and other normal activities within one to three months, depending on their overall health and progress during recovery.
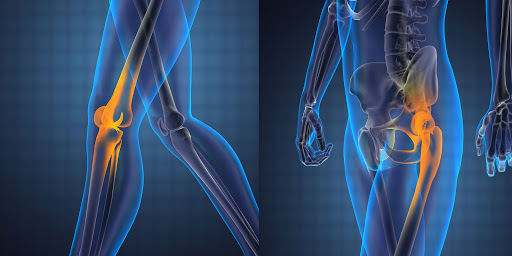
Knee Prosthesis
The most prominent reason in knee joint deterioration is wear and tear. Obesity, rheumatic diseases cause early wear of the knee. Genetic predisposition can have an effect on knee wear and tear. Physical trauma history or repetitive minor traumas are the reasons for wear on the knee. Joint damage is more common in those who regularly do heavy sports, and arthritis is more common in their joints. Women, especially those over the age of 55, experience knee problems more often compared to men. Knee problems are more common in people who have some blood diseases such as hemophilia and those who work by squatting heavily.
What does Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals offer patients?
How many specialists are there and what accreditation's have been awarded to Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals?
Arthroplasty or Knee Replacement is a surgical procedure involving the exchange of a damaged and weakened knee joint with an artificial one. It is commonly performed for different types of arthritic knee diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis mostly brought on by old age. Other causes can be accidents which lead to meniscal tears, joint dislocation, ligament tears, and cartilage damage. Osteoarthritis is the most common cause of knee replacement. Genu Valgus and Genu Varus can also be treated by surgery. Arthroplasty can either be partial (Partial Knee Replacement [PKR]) or complete (Total Knee Replacement [TKR]) depending upon the degree of damage.
The choice to proceed with a Knee Replacement is often brought on by ongoing discomfort and diminished mobility. This Knee Replacement involves a surgical procedure with the intention to diminish pain and revive the functionality of the joint.
6 weeks are required for complete recovery, however, it may take 3 months for inflammation and pain to subside and the knee continues to repair up to 2 years after the surgery. During the first 6 weeks, you cannot walk properly and experience pain and inflammation, therefore, walking aids such as walkers, crutches, walking sticks, etc. will be required. You can start walking again 12 to 24 hours of surgery with the help of your medical assistant. You can drive again 4 to 6 weeks after the operation. The replaced knee can work for 15 years after which metallic parts wear out and start causing problems. Note that the recovery from Knee Replacement is a gradual process and varies from person to person.
More than 90% of people who have gone through a knee replacement surgery told that they have a tremendous amount of relief in pain and their ability to walk around. 85 to 90% of surgeries are reported to be successful. 60% of these surgeries were undergone by women. The probability of positive outcomes hinges primarily on elements like the degree of injury, an individual's general wellbeing, and compliance with recovery and subsequent care.






































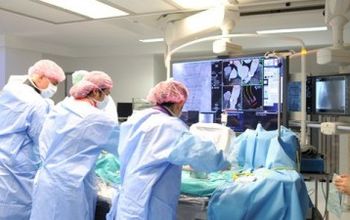



Hip and Knee Joint Replacement Surgery
Total joint replacement is a surgical procedure where parts of an arthritic or damaged joint are removed and replaced with a metal, plastic or ceramic device called a prosthesis or implant. The prosthesis is designed to reproduce the shape and motion of the normal joint.
A joint is an area in the body where two or more bones join together to allow motion. The surfaces of the bones are covered with cartilage to form a normal smooth gliding joint. Over time this cartilage can break down, leading to bone-on-bone friction which can cause inflammation and pain.
The most common conditions that lead to joint replacement surgery are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. There are, however, other causes of joint pain that may also lead to joint replacement including hereditary disorders, developmental problems, and trauma. Joint replacement is performed only after other conservative treatments have failed such as medications, physical therapy, and injections.
Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
We successfully perform partial and total joint prostheses in our Prosthetic Surgery Department. Total joint prosthesis aims to stabilize the joint by replacing the damaged joint surface with artificial materials and to eliminate existing pain. In recent years, total joint prosthesis practices having increasingly been performed in our country as in the whole world.
The joints where prosthetic surgery is mostly performed are knee and hip prostheses. It is also frequently used in the treatment of deformations in the cartilage surfaces of the joints due to arthritis, infections, rheumatic diseases, trauma, or congenital structural disorders.
We perform general anesthesia or local anesthesia (spinal and/or epidural) for our hip and knee replacement surgeries. We take the choices jointly with our patients. Generally, within the first 48 hours after prosthesis surgery, we get our patients to stand up and walk.
What Happens During Joint Replacement Surgery
Hip and knee replacement are two of the most commonly performed operations in orthopedic surgery. Both procedures are very successful at eliminating pain, correcting deformity and improving patient mobility so patients can regain quality of life and get back to the activities they enjoy.
During hip replacement, the damaged ball of the hip ball and socket joint is removed and replaced with a metal or ceramic ball that attaches to a stem that fits into the femur. The prosthesis is usually coated with a special material into which the bone will grow over time. In some instances, however, the prosthesis is cemented into the bone. The socket portion of the ball and socket joint is also replaced with a metal cup that is placed into the pelvis. A plastic liner is then snapped into the metal cup and rotates with the new ball on the end of the femoral stem. The prostheses and implants come in a variety of shapes and sizes that can be tailored to the individual.
During total knee replacement surgery, a thin amount of bone along the surface of the joint is removed from the end of the femur or thigh bone, the top of the tibia or leg bone, as well as the underside of the kneecap. The surfaces of the bone are then shaped with tools and sized to allow an appropriate implant fit for each individual knee. The major ligaments and tendons of the knee are typically kept in place to provide stability and normal motion of the knee joint. Like hip replacements, knee replacements can either be cemented into place or are covered in a special material into which the bone will grow.
Total joint replacement surgery usually takes one to two hours and is typically performed in a hospital setting with a one- to two-day hospital stay. The procedure is usually performed under spinal anesthesia in combination with a nerve block. This prevents the need for general anesthesia and intubation during the surgery and can help patients avoid many of the side effects of general anesthesia such as post-operative nausea. This allows for better pain control and quicker recovery.
Following the surgery and a short stay in the recovery room, patients will begin walking on the day of their surgery. The majority of patients are then sent home with instructions for further therapy. Typically, patients can return to work and other normal activities within one to three months, depending on their overall health and progress during recovery.

Knee Prosthesis
The most prominent reason in knee joint deterioration is wear and tear. Obesity, rheumatic diseases cause early wear of the knee. Genetic predisposition can have an effect on knee wear and tear. Physical trauma history or repetitive minor traumas are the reasons for wear on the knee. Joint damage is more common in those who regularly do heavy sports, and arthritis is more common in their joints. Women, especially those over the age of 55, experience knee problems more often compared to men. Knee problems are more common in people who have some blood diseases such as hemophilia and those who work by squatting heavily.
What does Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals offer patients?
How many specialists are there and what accreditation's have been awarded to Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals?









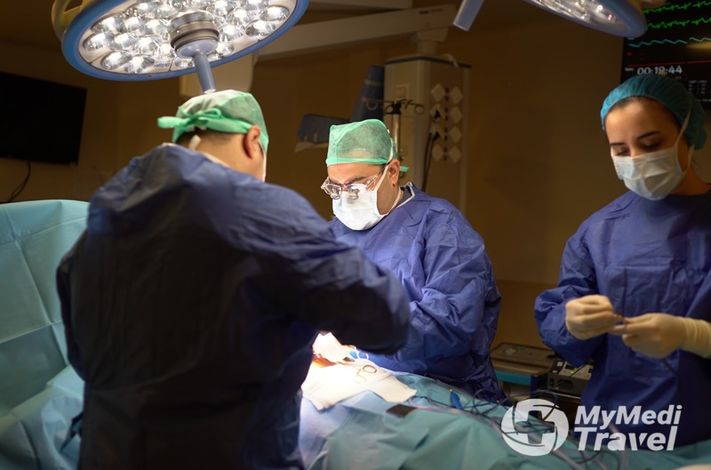
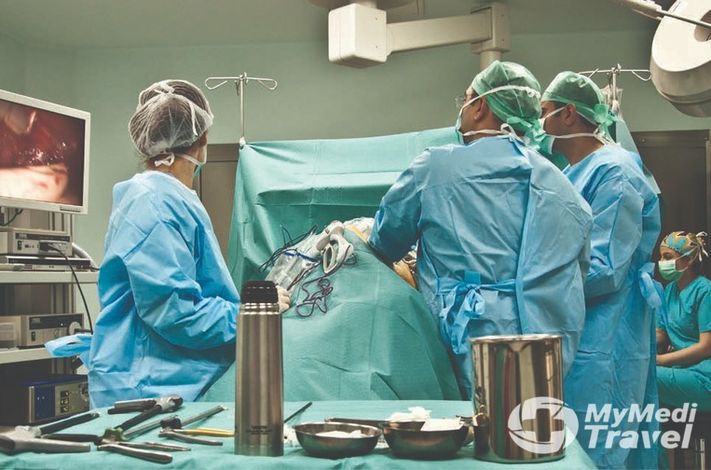









Hip and Knee Joint Replacement Surgery
Total joint replacement is a surgical procedure where parts of an arthritic or damaged joint are removed and replaced with a metal, plastic or ceramic device called a prosthesis or implant. The prosthesis is designed to reproduce the shape and motion of the normal joint.
A joint is an area in the body where two or more bones join together to allow motion. The surfaces of the bones are covered with cartilage to form a normal smooth gliding joint. Over time this cartilage can break down, leading to bone-on-bone friction which can cause inflammation and pain.
The most common conditions that lead to joint replacement surgery are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. There are, however, other causes of joint pain that may also lead to joint replacement including hereditary disorders, developmental problems, and trauma. Joint replacement is performed only after other conservative treatments have failed such as medications, physical therapy, and injections.
Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
We successfully perform partial and total joint prostheses in our Prosthetic Surgery Department. Total joint prosthesis aims to stabilize the joint by replacing the damaged joint surface with artificial materials and to eliminate existing pain. In recent years, total joint prosthesis practices having increasingly been performed in our country as in the whole world.
The joints where prosthetic surgery is mostly performed are knee and hip prostheses. It is also frequently used in the treatment of deformations in the cartilage surfaces of the joints due to arthritis, infections, rheumatic diseases, trauma, or congenital structural disorders.
We perform general anesthesia or local anesthesia (spinal and/or epidural) for our hip and knee replacement surgeries. We take the choices jointly with our patients. Generally, within the first 48 hours after prosthesis surgery, we get our patients to stand up and walk.
What Happens During Joint Replacement Surgery
Hip and knee replacement are two of the most commonly performed operations in orthopedic surgery. Both procedures are very successful at eliminating pain, correcting deformity and improving patient mobility so patients can regain quality of life and get back to the activities they enjoy.
During hip replacement, the damaged ball of the hip ball and socket joint is removed and replaced with a metal or ceramic ball that attaches to a stem that fits into the femur. The prosthesis is usually coated with a special material into which the bone will grow over time. In some instances, however, the prosthesis is cemented into the bone. The socket portion of the ball and socket joint is also replaced with a metal cup that is placed into the pelvis. A plastic liner is then snapped into the metal cup and rotates with the new ball on the end of the femoral stem. The prostheses and implants come in a variety of shapes and sizes that can be tailored to the individual.
During total knee replacement surgery, a thin amount of bone along the surface of the joint is removed from the end of the femur or thigh bone, the top of the tibia or leg bone, as well as the underside of the kneecap. The surfaces of the bone are then shaped with tools and sized to allow an appropriate implant fit for each individual knee. The major ligaments and tendons of the knee are typically kept in place to provide stability and normal motion of the knee joint. Like hip replacements, knee replacements can either be cemented into place or are covered in a special material into which the bone will grow.
Total joint replacement surgery usually takes one to two hours and is typically performed in a hospital setting with a one- to two-day hospital stay. The procedure is usually performed under spinal anesthesia in combination with a nerve block. This prevents the need for general anesthesia and intubation during the surgery and can help patients avoid many of the side effects of general anesthesia such as post-operative nausea. This allows for better pain control and quicker recovery.
Following the surgery and a short stay in the recovery room, patients will begin walking on the day of their surgery. The majority of patients are then sent home with instructions for further therapy. Typically, patients can return to work and other normal activities within one to three months, depending on their overall health and progress during recovery.

Knee Prosthesis
The most prominent reason in knee joint deterioration is wear and tear. Obesity, rheumatic diseases cause early wear of the knee. Genetic predisposition can have an effect on knee wear and tear. Physical trauma history or repetitive minor traumas are the reasons for wear on the knee. Joint damage is more common in those who regularly do heavy sports, and arthritis is more common in their joints. Women, especially those over the age of 55, experience knee problems more often compared to men. Knee problems are more common in people who have some blood diseases such as hemophilia and those who work by squatting heavily.
What does Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals offer patients?
How many specialists are there and what accreditation's have been awarded to Group Florence Nightingale Hospitals?
CONTACT SUCCESSFUL