Laryngoscopy in Tu Son
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Laryngoscopy in Tu Son



































































































































No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reach out to the top clinics all at once
What does a Laryngoscopy Procedure Involve?
The laryngoscopy procedure may be done in different ways. There are a few options such as indirect laryngoscopy, direct fiber-optic laryngoscopy, and direct laryngoscopy.
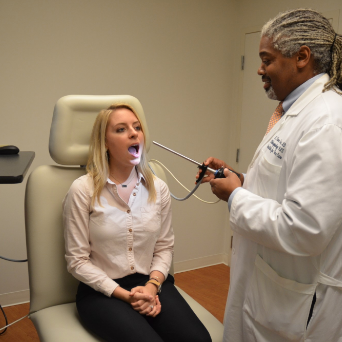
In indirect laryngoscopy, you will sit up straight on a high back chair. Local anesthesia or numbing medicine will be sprayed on your throat so you will not feel anything. Your tongue will be covered with gauze and will be moved to one side to stop it from blocking your doctor’s view. Your doctor will then insert the small mirror into your throat and explore the area. Although your throat is numbed, having a mirror inserted into your throat may still make you gag. Sometimes, your doctor may ask you to make a certain sound in order to make your larynx move. If your doctor found a foreign object in your throat, they will remove it.
Sometimes called flexible laryngoscopy, direct fiber-optic laryngoscopy uses a small telescope attached at the end of a cable, which can go up to your nose and down into your throat. In this type of laryngoscopy, your doctor will give you a numbing medicine for your nose so you will not feel anything. In some cases, your doctor may use a decongestant to open your nasal passages. As in indirect laryngoscopy, you may gag during direct fiber-optic laryngoscopy as well.
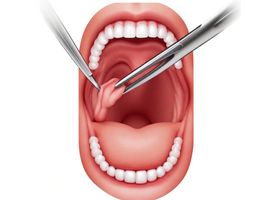
Direct laryngoscopy is the most involved type of laryngoscopy. During this procedure, your doctor will push a laryngoscope (a small hand tool that allows your doctor to look into your larynx and other surrounding areas of your throat) down your tongue and lift up the epiglottis. The epiglottis is the flap of the cartilage covering your windpipe that closes during swallowing and opens during breathing. Your doctor may remove small growths or tissue samples for testing (biopsy). They can also use direct laryngoscopy to insert a tube into your windpipe to help you breathe during surgery or in an emergency. With this type of laryngoscopy, you will be given general anesthesia.
How Long Should I Stay in Tu Son for a Laryngoscopy Procedure?
The stay period in Tu Son for a Laryngoscopy can widely differ depending on personal situations. Usually, Laryngoscopy is an outpatient process, suggesting that patients often leave on the same day. Since the results will usually be available within a few days, it is advisable that you stay in Tu Son for 3 to 7 days. Once the results are ready, you will have to visit your doctor to discuss the results. Considering potential follow-up visits that might need a more extended stay is also crucial.
What's the Recovery Time for Laryngoscopy Procedures in Tu Son?
It's crucial to understand that recovery can be quite swift, with many patients able to return to normal activities within a day or two. However, some patients may experience a sore throat, mild discomfort, or hoarseness for a few days after the procedure. Those symptoms can generally be managed with over-the-counter pain medication, rest, and consuming plenty of fluids.
Your throat may be slightly swollen or feel sore for around 2 to 5 days. You may also notice that your voice sounds hoarse. This may resolve within 1 to 8 weeks. You may be asked to speak as little as possible for a week or two. Therefore, if your job requires using your voice, you should take 1 to 2 weeks off work.
What sort of Aftercare is Required for Laryngoscopy Procedures in Tu Son?
Your doctor will give you detailed instructions on what you can and cannot do during your recovery time. Since your mouth and throat will be numb for a couple of hours following the procedure, you will not be allowed to drink or eat anything until the numbness subsides. Your throat may be sore once the numbness wears off. You can gargle with salt water or suck on ice to ease it. Your doctor may also recommend you to take over-the-counter pain relievers.
Keeping an open line of dialogue with your medical practitioner is paramount, informing them of any uncommon symptoms like extended discomfort, trouble with swallowing, or breathing irregularities. Part of your post-treatment care includes routine check-ins, during these sessions, your health provider will track your recovery and deliberate the result of the operation.
What's the Success Rate of Laryngoscopy Procedures in Tu Son?
Recognizing that the Laryngoscopy serves primarily as a diagnostic technique rather than a curative measure is crucial. Usually, its efficacy can be gauged by its capacity to accurately pinpoint disorders impacting the larynx. Broadly speaking, the Laryngoscopy boasts an impressive success rate in accomplishing its chief objective of rendering a comprehensive perspective of the larynx. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of any follow-up treatments hinges on the specific diagnosed condition, the selected therapeutic course, and personal patient factors. In the aspect of detecting cancer, the procedure is hailed for its 100% precision rate.
Are there Alternatives to Laryngoscopy Procedures in Tu Son?
The alternative to laryngoscopy depends on the reason why you need it. Sometimes, your doctor may recommend laryngeal electromyography (laryngeal EMG) as the alternative. With a laryngeal EMG, the muscle activity in the vocal cords and throat are assessed. Another procedure called esophagogram, also called a barium swallow, can also be used. In esophagogram, patients drink a small amount of barium prior to the test and an X-ray is used to see the structure and function of the esophagus during swallowing.
However, these alternatives may not provide the same level of detail or allow for the same diagnostic possibilities as the Laryngoscopy. Thus, the choice of procedure will depend on individual needs and circumstances.
This information has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, however, we strongly recommend you to consult with your doctor before pursuing medical procedures overseas.