Full Body CT Scan in Ha Long
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Full Body CT Scan in Ha Long



































































































































No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reach out to the top clinics all at once
What does a Full Body CT Scan Procedure Involve?
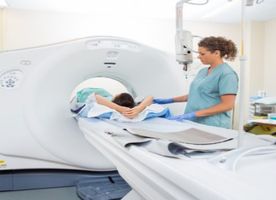
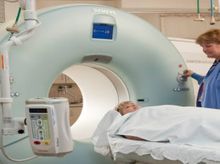
During a full-body CT scan, you will have to lie flat on your back on a motorized table that can slide through the doughnut-shaped CT scanner machine. Straps, pillows, and a special cradle may be used to help you stay in the correct position and remain still during the exam. In some cases, a contrast material may be used. It will be injected through an intravenous line (IV) or swallowed.
To determine the correct position for the scans, the table will move quickly through the scanner. Then, during the actual CT scanning, the table will move slowly through the machine and it may take several passes. When the motorized table moves you into the machine, the X-ray tube and detectors will rotate around you. Several images of thin slices of your body are taken in each rotation. The images are then sent to a computer, where they are combined to
The radiographer will operate the machine from a separate room. They can see and hear you, and you will be able to communicate with them during the scan via intercom. They may ask you to hold your breath at certain parts of the scan because you need to stay completely still. Any motion, including body movements and breathing, can blur the scan images. The radiographer may also lower, raise, or tilt the table to create the correct angle for the X-rays.
No anesthesia is involved in a full-body CT scan as it is not painful. However, children who cannot stay still may be sedated.
How Long Should I Stay in Ha Long for a Full Body CT Scan Procedure?
You may be allowed to leave the hospital on the same day as your full-body CT scan. However, since the results will not be given to you immediately, it is advisable that you stay in Ha Long for 5 to 7 days, or until the results are ready. Once the results are ready, you will have to attend a follow-up appointment to discuss them with your doctor.
What's the Recovery Time for Full Body CT Scan Procedures in Ha Long?
Full-body CT scans do not require any recovery time. You can return to your daily activities, go to work, drink, drive, eat, and drink as normal straight away.
What sort of Aftercare is Required for Full Body CT Scan Procedures in Ha Long?
If a contrast material is used, you will have to drink lots of fluids to help your kidneys flush out the contrast material from your body. If not, there are no restrictions or special aftercare following the procedure.
What's the Success Rate of Full Body CT Scan Procedures in Ha Long?
A full-body CT scan has the potential to be inaccurate. A cancer diagnosis based on a CT scan has up to 30% inaccuracy rates. In addition, the procedure is not recommended for those without symptoms.
A full-body CT scan carries some potential risks. During the procedure, your body will be exposed to ionizing radiation. While low doses of radiation in the procedure have not been revealed to cause any harm in the long-term, much greater doses may slightly increase your risk of cancer. The procedure can also harm unborn babies. Therefore, make sure to tell your doctor if you are pregnant.
In some cases, the contrast material can cause allergic reactions, which may result in a rash or itchiness.
Are there Alternatives to Full Body CT Scan Procedures in Ha Long?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans is the main alternative to a full-body CT scan. MRI scans are currently being evaluated for their possible value in screening. One major benefit of the procedure is that they do not expose you to ionizing radiation. However, they tend to be more expensive than a full-body CT scan.
This information has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, however, we strongly recommend you to consult with your doctor before pursuing medical procedures overseas.