Coronary Angioplasty in Ludwig Erhard Strasse
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Coronary Angioplasty in Ludwig Erhard Strasse













































































































































No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reach out to the top clinics all at once
What does a Coronary Angioplasty Procedure Involve?
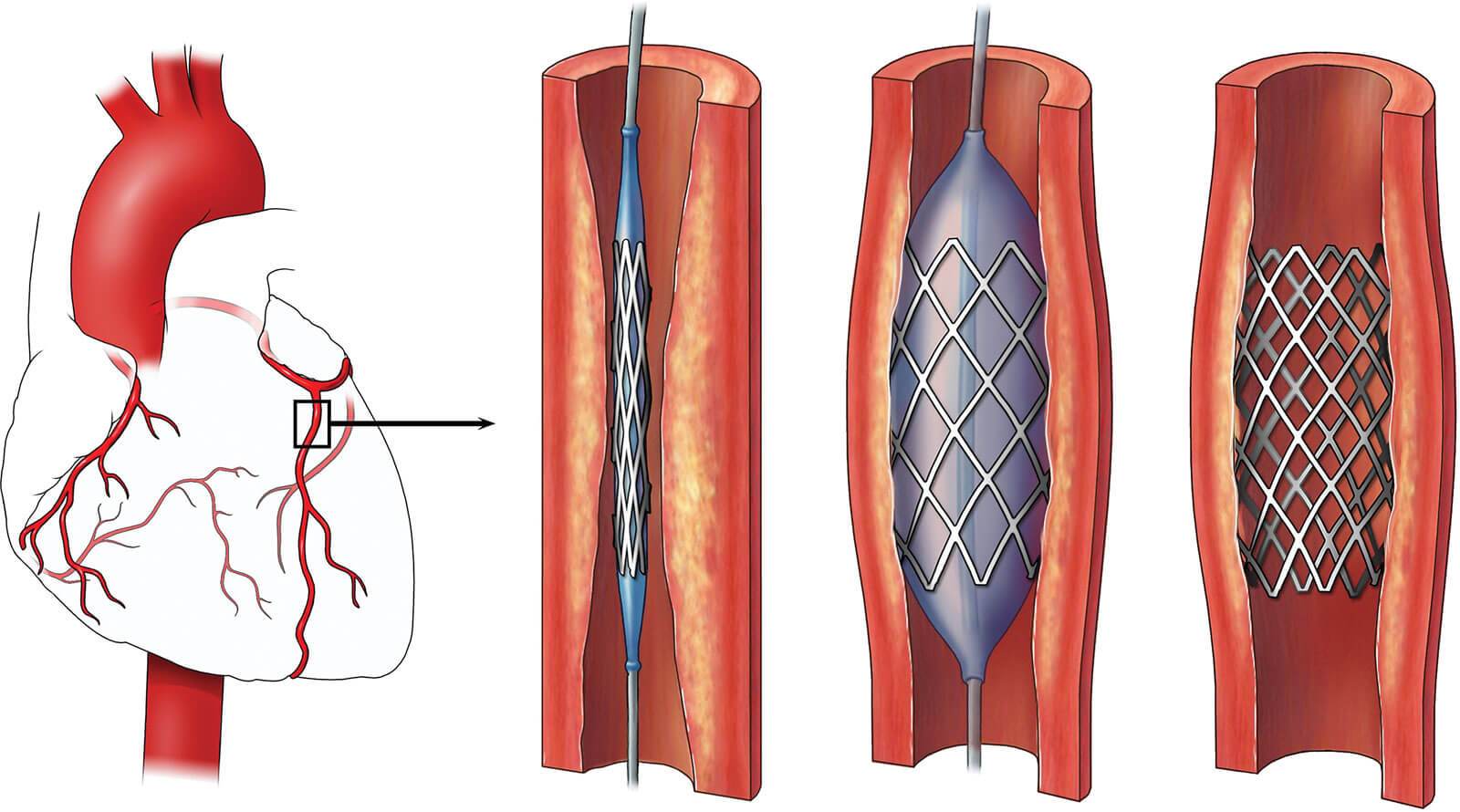
The Coronary Angioplasty is a mildly intrusive process primarily intending to resume a regular flow of blood to the heart. To begin, the doctor uses local anesthesia to numb the target area. A minor cut is induced in the patient's body, typically at the wrist or groin, via which a catheter bearing a minute balloon on one end is inserted. This catheter is manipulated until it reaches the obstructed artery.
Once the catheter is properly positioned, the balloon is inflated to help dislodge the obstruction, thereby facilitating a pathway for blood circulation. Frequently, a stent (a small tube resembling a mesh) is introduced at that spot to maintain the artery's openness. Depending on the complexity and quantity of obstructions to be addressed, the procedure's duration can vary from 30 minutes to a few hours.
How Long Should I Stay in Ludwig Erhard Strasse for a Coronary Angioplasty Procedure?
Typically, Coronary Angioplasty is an ambulatory procedure, implying that patients are permitted to return home on the same day, following a period of monitoring at the healthcare facility. Nevertheless, under certain circumstances, it might be necessary for patients to stay overnight or longer at the hospital for observation, particularly if they have substantial concurrent health issues or if any issues occur during the procedure.
In Ludwig Erhard Strasse, renowned healthcare centers suggest patients remain in the local area for an approximate duration of one week following the procedure. This facilitates a return consultation for health assessment post-procedure and allows for tracking of the recovery progression. Also, it assures immediate access to medical services should any complications arise after the procedure. It's advised that patients communicate with their healthcare provider to receive recommendations tailored to their unique circumstances.
What's the Recovery Time for Coronary Angioplasty Procedures in Ludwig Erhard Strasse?
The recovery period following a Coronary Angioplasty can differ among individuals, though generally, most can anticipate returning to their regular activities within a week. In the recovery phase, patients may experience fatigue and slight unease in the area of catheter entry.
During this healing time, the emphasis should be on heart health. This involves adhering to a heart-friendly diet, engaging in doctor-recommended regular physical exercises, managing stress effectively, and refraining from tobacco use. It's also vital to comply with all medication instructions to avoid the formation of blood clots and manage any pre-existing conditions such as hypertension or high cholesterol levels.
What sort of Aftercare is Required for Coronary Angioplasty Procedures in Ludwig Erhard Strasse?
Ensuring appropriate post-care following a Coronary Angioplasty is vital for optimal recuperation and sustained well-being. It is typically mandatory for patients to partake in periodic assessments, allowing medical practitioners to oversee their recovery and alter treatment plans or lifestyle guidelines when necessary.
Besides routine examinations, maintaining a punctual medication routine, adhering to a diet conducive to heart health, routine physical activity, and abstaining from tobacco use are also compulsory for patients. The possibility of suggesting a heart recuperation program could also be considered, providing the requisite knowledge and assistance during the recovery phase. It's crucial to bear in mind that while Coronary Angioplasty bolsters blood circulation, it doesn't provide a complete remedy for coronary heart disease. Hence, perpetual care is necessary to control the illness and avert potential cardiac complications.
What's the Success Rate of Coronary Angioplasty Procedures in Ludwig Erhard Strasse?
Research shows that Coronary Angioplasty is a highly successful treatment for coronary heart disease. In fact, the procedure is successful over 95% of cases, according to the NHS. Success, in this case, is defined as significantly improved blood flow to the heart muscle and considerable relief from symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath. However, the long-term success of a Coronary Angioplasty often depends on the individual's commitment to lifestyle changes and medication adherence.
It is also important to note that not every patient with coronary heart disease is a suitable candidate for the procedure. Factors such as the location and extent of the blockage, the patient's overall health, and whether or not they have had previous heart surgery play an important role in the potential success of the Coronary Angioplasty.
Are there Alternatives to Coronary Angioplasty Procedures in Ludwig Erhard Strasse?
Indeed, multiple alternatives to Coronary Angioplasty exist, contingent on the degree and intensity of coronary heart disease. For a proportion of people, alterations in lifestyle, such as improved dietary habits, frequent physical activity, and medicinal therapy can help manage symptoms and hinder disease escalation.
An additional alternative that could be contemplated is Coronary Artery Bypass Graft surgery (CABG). In this procedure, a healthy artery or vein from another part of the body is grafted (affixed) to the obstructed coronary artery, which establishes a new route for blood to reach the heart muscle. Nevertheless, this procedure is a substantial surgery and is typically reserved for more severe cases when alternative treatment strategies have proven unsuccessful or are not suitable.
This information has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, however, we strongly recommend you to consult with your doctor before pursuing medical procedures overseas.